Climate-resilient bioeconomy in the value-added cycle of wood and other renewable raw materials
The Rosenheim Technical University of Applied Sciences is researching the material use of climate-resilient wood and biomass. The focus here is on the processing of new types of wood and waste wood as well as the recycling of the products obtained from them and their recyclability using digital methods and AI.
Project background
Wood is the most important domestic raw material in Germany and, alongside other renewable resources, is an essential component for a sustainable bioeconomy. Wood has the potential to contribute significantly to the transformation from a fossil to a regenerative economy. At the same time, the forest must change, because climate change is severely affecting existing forests. Climate damage and calamities are the result.
The conversion of forests from conifers to climate-resistant mixed and deciduous forests is therefore becoming increasingly urgent. The industry will therefore have to deal with new types and assortments of wood and inferior qualities from damaging events. In addition, the available wood supply has been greatly reduced by forest conversion and damaging events.
The material use of new wood species and waste wood in technical applications such as high-quality composite materials and components is therefore necessary. In addition, new products and their components without an existing recycling concept are not usable any longer in a sustainable industry. Material waste wood cycles must be developed in order to make greater use of the carbon sequestration in wood and reduce the harvesting pressure on forests.
Project objective
The aim is to develop expertise in the processing value chain of new types of wood and the material utilization of waste wood for transfer to research and teaching. This project therefore focuses on the technical processing of new types of wood and secondary waste wood assortments and qualities by means of mechanical and thermomechanical processing and recycling methods.
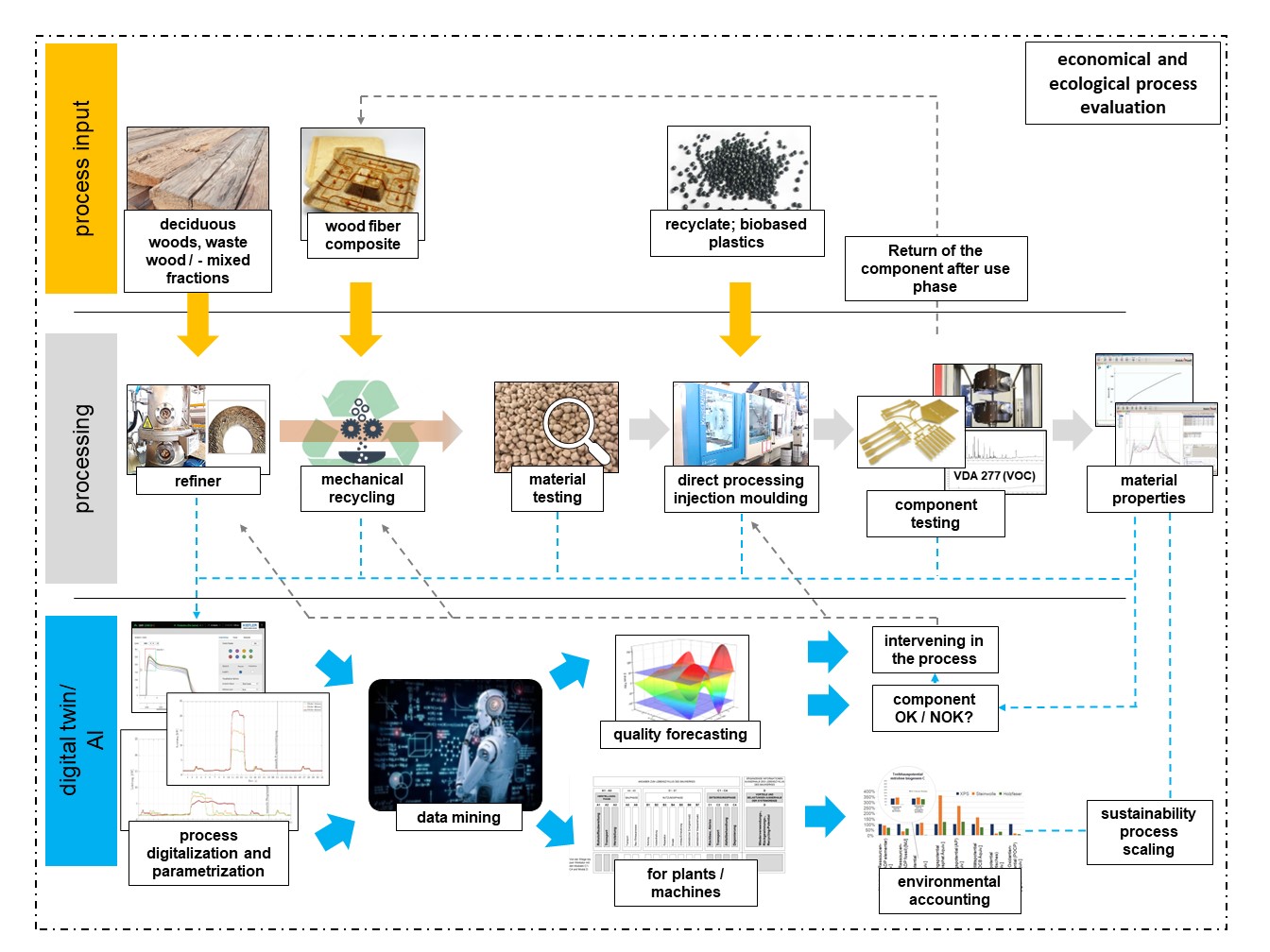
Furthermore secondly, digital data is used to parameterize the processes in order to scale processes and evaluate them in terms of sustainability as well as to optimize process management using AI-based approaches and to analyze possible applications for material development (Figure 1). In addition, when using secondary raw materials, especially the pollutants, impurities and volatile components (VOCs) are considered, which can be an obstacle in the cascade utilization.
Project procedure
Innovation
With the work of the proposed focus, it will be possible to strengthen the sustainable use of primary materials and the recycling of wood composites. This will be achieved in particular through the characterization of new material systems and new wood-based composite materials.
Thereby new wood species resulting from forest conversion, as well as the new wood assortments and qualities from waste and damaged wood, are made available for various applications and products. Process chains examined in the project are the pulping of the wood and the further processing into wood-based composites (such as insulation boards) as well as the further processing of plastics into technical fiber composite components (such as automotive applications).
Based on digital data and supported by artificial intelligence, the new manufacturing processes can be scaled and evaluated ecologically and economically. This makes it possible to derive potential for improvement and to optimize the procedures for processing new wood assortments directly during their development.
Strengthening the closed-loop recycling of wood composites and the material utilization of waste wood offers the potential to manufacture products with a great depth of value, a low fossil resource intensity and a high CO2 reduction potential. This means that this focus makes a significant contribution to the climate neutrality, a government's goal by 2050, and to the objectives of the Bavarian bioeconomy strategy (including the reduction of fossil resource consumption, protection of domestic and renewable resources, cascade utilization).
Overall lead for THRO input
Sub-project lead
Project staff
T +49 (0) 8031 / 805 - 2636 Sebastian.Wiedl[at]th-rosenheim.de
ORCID iD: 0009-0003-9099-1046
T +49 (0) 8031 805-2868 theresa.pscherer[at]th-rosenheim.de
ORCID iD: 0009-0006-0549-1605
T +49 (0) 8031 / 805 - 2760 Thomas.Schmid[at]th-rosenheim.de
michaela.sehy[at]th-rosenheim.de
Project duration
2024-01-01 - 2027-12-31Project funding

Funding programme
Programm zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung und Entwicklung an Hochschulen für angewandte Wissenschaften - Fachhochschulen